TABLE OF CONTENT
When you play a sport or do something athletic, you are likely to get a sport injury. Bones, soft tissues and muscles, all can be affected by it. Apart from physical health, they also impact mental health. The psychology of sport injury plays a big part in how athletes heal. This is why they must focus on their mental health too. Injury recovery takes time, and athletes may face issues of fear, sadness, and stress.
Dr Ahrendt claims that sports injuries affect your mental health on many different levels. He states that the psychological effects of injury vary with how much your identity is tied to sport. He also claims the effects to be higher in athletes of college teams.
Exploring the psychology of sport injury is the key to helping athletes recover fully. This blog will cover everything you need to know about the psychology of sport injuries and their impacts.
Psychology of Sport Injury? All You Need to Know
The psychology of sport injury refers to how injuries affect the mental health of athletes. Athletes face a mental struggle during recovery. They feel stressed and worried. They fear they won’t be able to reach their peak form again. These struggles can delay the recovery. Psychology and injuries are, thus, closely tied.
Learn the role of physiotherapy in recovery, here.
Sports Injury and Mental Strain
Athletes are usually concerned about their health since there are high-risk sports. The following are such sports:
- Rugby or Football (American)
- Gymnastics
- Boxing and Mixed Martial Arts (MMA)
- Skiing and Snowboarding
- Ice Hockey
- Wrestling
- Motorsports (e.g., motocross, car racing)
- Cheerleading
- Equestrian Sports (Horseback Riding)
- Diving
- Skateboarding
- Rock Climbing
- Surfing
- Cycling (especially mountain biking or racing)
Psychology of sports injury makes them fear they won’t return to full form. This mental strain is part of the psychology of injury. It can lead to doubt as well as fear.
How injuries affect athletes mentally
The psychological effects of injury can last for a long time. The body itself may heal but the brain may not heal quickly. When injuries occur the athletes feel lost and overwhelmed. Such emotions impact the recovery rate.Athletes also slow down since they are feeling despair. The psychological impact of injuries in athletes, thus, has many aspects. They should all be cared for.
“Initial responses to injury often involve emotional distress, which can influence the recovery process and future performance. Psychological challenges during rehabilitation can include stress, lack of coping mechanisms, and motivational issues, which can hinder an athlete’s ability to engage fully in the recovery process.”
Adeera Azam et al.
Effects of injuries on athletes
The psychology of injured athletes can shift to a great extent. They are separated from their goals, routines, and identities that they have built around their sport. This creates a sense of loss beyond their playing fields. It also triggers a range of emotional responses and internal struggles. Some of the aspects of the psychology of sport injury in athletes are as follows:
Depression:
Sports injuries often result in depression. Athletes have their identity linked with the sport. Not being able to play can generate a feeling of deep loss. A sense of loneliness may also overcome them. This is because they are away from their team as well as the sport. It can further evoke the following feelings:
- Hopelessness
- helplessness
- worthlessness
Case study:
The case study entails Lindsey Vonn who is a ski racer. A range of awards was granted to her. She faced many physical injuries during her career and their psychological impact as well. She has faced depression for a long time. She revealed that her depression was triggered by the following:
- Injuries like ACL tears
- Long recovery periods
- Missing major events (the 2014 Sochi Olympics)

She admitted to living with depression in silence for about a decade. She also used skiing as an escape from her negative thoughts. Her serious injuries, surgeries and nerve damage led to an increased feeling of isolation and sadness. She sought help and used her athlete mindset in recovery. Now retired, she still emphasises emotional well-being and wellness.
Anxiety:
Anxiety is another major part of the psychology of sport injury that players can feel. It is fueled by the following thoughts:
- How long will the healing take?
- Will they ever play the sport again?
- Will I perform the same way or not?
- They might fear missing out on important games or events.
- They may also fear losing their spot on the team.
Anger:
Athletes may feel angry over the entire situation. Anger is created over the unfairness of the whole thing. If you are an athlete, you may ask why me? You could also keep thinking if you could stop it. Doing something differently in the moment is another all-consuming thought. Anger often turns to resentment towards the following:
- Coaches
- Teammates
- Sport
This aspect of the psychology of sport injury can lead to other issues as well.
PTSD:
Athletes can experience injury as a traumatic experience. Some such cases would be if the injury was intensely painful or it had graphic visuals, such as compound fractures. There can also be trauma attached if it occurred in a high-stakes competition. The symptoms can include the following:
- Flashbacks of the injury event.
- Avoiding all aspects traumatic event
- Hyperarousal (i.e. exaggerated startle responses)
- Sleep disturbances
- intrusive thoughts.
For instance, an athlete tears an ACL in a critical game. This part of the psychology of sport injury would lead to an intense fear of the same injury. This is especially visible when they play the next time.
Get useful insights about PTSD Treatment.
Kinesiophobia:
It refers to an intense fear of re-injury. This may happen even after the athlete is completely recovered. This effect is often seen in high-impact sports. For instance, football and gymnastics players can encounter it. The reason for this is the sudden nature of the injury. The severity of the injury is also a reason.
The fear shows in the following ways:
- Hesitation in movements or avoiding certain drills
- Reduced performance due to caution
- Psychological distress before or during games
Disordered Eating
Athletes have specific body composition. Their metabolism and training intensity are also different from other people. Injuries may disrupt them. In a bid to deal with this, the athletes engage in unhealthy eating habits. This effect is common in aesthetic sports. It also appears in weight-related competitions. These include figure skating, ballet, wrestling, etc.. The following negative thoughts fuel this disorder:
- Fear of weight gain during inactivity.
- Pressure to maintain a certain physique or weight class.
- Loss of appetite due to emotional stress.
Substance Misuse
Athletes who are facing an injury and suffering psychologically may turn to addiction. This leads to worsening of mental health in the long run. Some of the drugs that athletes can use are:
- Painkillers
- Alcohol
- Cannabis
- Performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs)
To relieve the emotional or physical pain, they can begin abusing any of those drugs. This drug abuse may develop to permanent dependence unless properly advised.
Post-Athlete depression and identity crisis
After an injury, athletes may get post athlete depression. It also occurs commonly after early retirement. This is a real mental challenge. When an athlete can’t play, they feel a loss of identity. Sport is something that defines their identity. When it is taken away, they may feel sad, anxious, and confused about what’s next. Post-athlete depression needs care and attention.
Psychological Symptoms
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Detachment
- Withdrawal
- Substance abuse
- Self-medicating
- Low self-esteem
- Despair
- Difficulty adjusting to non-sport environments
Mental Strategies Used in the Psychology of Sport Injury
Psychological approaches to sports injury rehabilitation are helpful in making athletes feel relaxed. Therapies help athletes deal with emotions. It also assists them in rebuilding their confidence. Some of the commonly used therapy approaches are as follows:
1. Psychotherapy
Among the talk therapies, psychotherapy or CBT is one of the most common ones. In this, your therapist helps you change your way of thinking. For athletes, it helps them manage their thoughts. A therapist talks to them. They help the athletes spot negative thoughts. After this, they turn these thoughts into positive ones.
Explore more about What is CBT UK
Why it matters:
Since negative thoughts slow down recovery, CBT is useful since it mitigates those thoughts.
Example:
A common negative thought is I won’t ever get better. After CBT, it can be turned into I am healing every day.

2. Mindfulness and other relevant techniques
Mindfulness is one great approach for athletes. It urges you to focus your awareness on the moment. This process is repeated multiple times to ensure that you are entirely present. These techniques help athletes stay relaxed. They also increase focus. Here are some examples of this kind of therapy.
Examples
Mindfulness:
You stay in the moment by paying attention to breathing.
Muscle relaxation:
In this, you tighten and relax muscles to release tension.
Calming images:
You picture the most relaxing place you can think of. It can be a forest or a beach or anything else.
How it helps
- Stops stress about the past or future.
- Helps with pain and sleep.
- Makes rehab feel easier and more peaceful.
Explore our blog to learn more about psychological therapy
3. Motivational Interviewing (MI)
MI is a type of counselling that helps you deal with a change. It helps you work through mixed feelings and find your own reasons to move ahead. For athletes, it helps them identify their motives to go ahead with rehab. The therapist listens and questions them. Athletes discover what is truly important to them during these questions.
Why it matters:
Injury often makes athletes lose focus. MI helps increase their self-confidence. It also assists them in clarifying their future goals and staying on track.
4. Visualisation and Mental Imagery
This technique is basically a practice of using your imagination to picture your success. For athletes, it is useful in visualising themselves playing and training. They can also picture themselves healing. This process is very helpful in preparing them mentally for their next game.
Why it works:
- The brain treats mental practice like real practice.
- It builds confidence, reduces fear, and helps performance.
- It increases mental strength to deal with nervousness in the game.
5. Group therapy
In group therapy, there is a small group of people with similar issues. They are led by a therapist. In the sessions, everyone shares their feelings and listens to others. In the context of sports injuries, members who have injuries and related mental issues can support each other. This decreases loneliness. Support groups and group therapy provide:
- Validation of feelings
- Shared coping strategies
- Hope and motivation
The Role of Coaches in Mental Recovery
A good coach helps in an athlete’s mental recovery. A coach who gives no support increases stress and fear of the athlete. A good coach can boost motivation and help athletes heal. Considering the psychology of sport injury, their role is crucial. Here are some of the roles coaches can play:
- Process grief, anger, or fear
- Cope with identity loss
- Set realistic recovery goals
- Maintain mental discipline throughout physical rehab
Learn more about sports injury rehabilitation here.
Stages of psychological recovery
The psychology of sport injury states that the recovery process for athletes takes time and involves stages. Each stage involves different emotions. Here is how coaches can help through every one of them:
- Shock and Denial:
This is the first stage. In this, athletes often deny their injury. They might try to push through the pain and avoid dealing with it. This stage can cause delays in accepting the need for rest. Here, coaches can help them understand their injury.
- Anger and Frustration:
As the injury sinks in, athletes can feel upset and angry. They become frustrated because of their inability to play and feel upset. This can lead them to feel weak. Here, coaches can make them focus on healing. This can lower such thoughts.
- Bargaining:
Athletes may start to bargain with themselves or others, trying to find ways to heal faster. They might promise to work harder or make deals in hopes of a quick return. Again, coaches have to walk through the entire healing process. They should explain that there are no shortcuts.
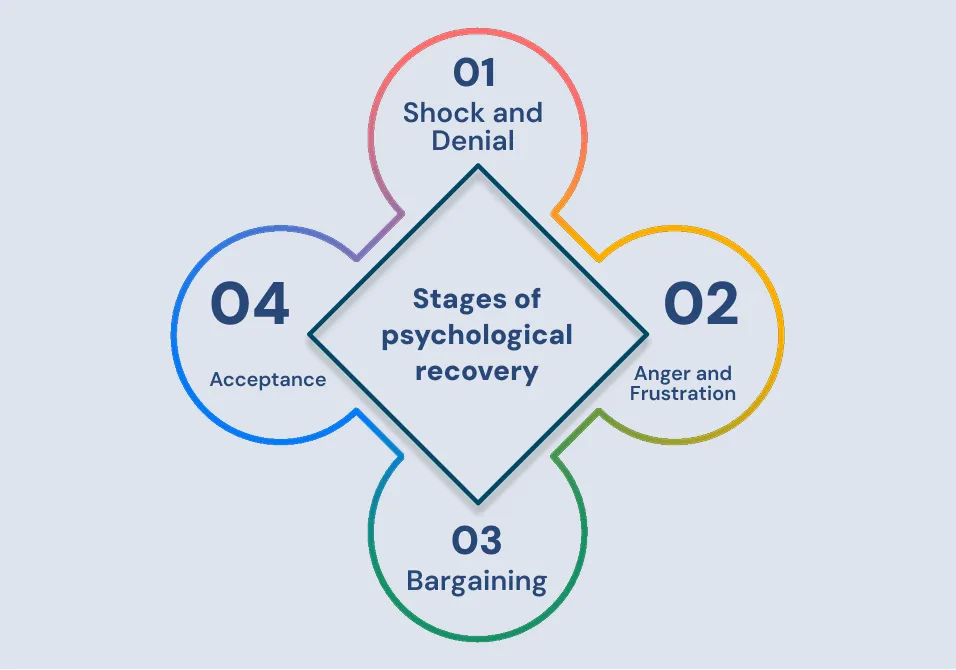
- Acceptance:
Over time, athletes begin to accept reality and focus on small steps to improve. Setting new goals helps them move forward. Another tip is to follow the recovery plan. Coaches can encourage them in these steps.
Role of teammates in the psychology of sport injury
A close team can help ease feelings of isolation. This makes recovery less stressful. Athletes are more likely to stay motivated when they have both coaching and teammate support during the healing process. Teammates can also offer the following for better recovery:
- Emotional support
- Encouragement
- Understanding
How Sports Injury Expert Witnesses Help
A sports injury expert witness can explain the mental side of an injury. They play a vital role in legal cases. They show how the psychological impact of injuries in athletes goes beyond the body. This expert help is key to understanding the full picture of recovery.
These witnesses have detailed knowledge about sports injuries. This includes sports medicine, diagnosis, treatment, etc. They also have experience in looking after such cases. They can explain the cause of injury, its extent and the long-term effects of the injury.
Their insights on the psychology of sport injury are valuable in multiple ways. They create a positive environment where athletes feel safe to express concerns. They explain the entire situation to the court. They also share their expert opinions on the matter. They also provide expert reports that contain their findings.
How can Concise Medico support the psychology of sport injury
The key to recovery is understanding the psychology of sport injury. Athletes require both mental and physical treatment. Emotional stress can slow down recovery. Thus, addressing the mental side of healing is crucial. We at Concise Medico support you throughout your healing journey. We provide you with a wide range of sports therapies. We make sure to cater to all aspects of the psychology of sport injury.
Contact us to seek help for psychology of sport injury
FAQs
When you play a sport or do something athletic, you are likely to get a sport injury. Bones, soft tissues and muscles, all can be affected by it. Apart from physical health, they also impact mental health. The psychology of sport injury plays a big part in how athletes heal. This is why they must focus on their mental health too. Injury recovery takes time, and athletes may face issues of fear, sadness, and stress.
Dr Ahrendt claims that sports injuries affect your mental health on many different levels. He states that the psychological effects of injury vary with how much your identity is tied to sport. He also claims the effects to be higher in athletes of college teams.
Exploring the psychology of sport injury is the key to helping athletes recover fully. This blog will cover everything you need to know about the psychology of sport injuries and their impacts.
Psychology of Sport Injury? All You Need to Know
The psychology of sport injury refers to how injuries affect the mental health of athletes. Athletes face a mental struggle during recovery. They feel stressed and worried. They fear they won’t be able to reach their peak form again. These struggles can delay the recovery. Psychology and injuries are, thus, closely tied.
Learn the role of physiotherapy in recovery, here.
Sports Injury and Mental Strain
Athletes are usually concerned about their health since there are high-risk sports. The following are such sports:
- Rugby or Football (American)
- Gymnastics
- Boxing and Mixed Martial Arts (MMA)
- Skiing and Snowboarding
- Ice Hockey
- Wrestling
- Motorsports (e.g., motocross, car racing)
- Cheerleading
- Equestrian Sports (Horseback Riding)
- Diving
- Skateboarding
- Rock Climbing
- Surfing
- Cycling (especially mountain biking or racing)
Psychology of sports injury makes them fear they won’t return to full form. This mental strain is part of the psychology of injury. It can lead to doubt as well as fear.
How injuries affect athletes mentally
The psychological effects of injury can last for a long time. The body itself may heal but the brain may not heal quickly. When injuries occur the athletes feel lost and overwhelmed. Such emotions impact the recovery rate.Athletes also slow down since they are feeling despair. The psychological impact of injuries in athletes, thus, has many aspects. They should all be cared for.
“Initial responses to injury often involve emotional distress, which can influence the recovery process and future performance. Psychological challenges during rehabilitation can include stress, lack of coping mechanisms, and motivational issues, which can hinder an athlete’s ability to engage fully in the recovery process.”
Adeera Azam et al.
Effects of injuries on athletes
The psychology of injured athletes can shift to a great extent. They are separated from their goals, routines, and identities that they have built around their sport. This creates a sense of loss beyond their playing fields. It also triggers a range of emotional responses and internal struggles. Some of the aspects of the psychology of sport injury in athletes are as follows:
Depression:
Sports injuries often result in depression. Athletes have their identity linked with the sport. Not being able to play can generate a feeling of deep loss. A sense of loneliness may also overcome them. This is because they are away from their team as well as the sport. It can further evoke the following feelings:
- Hopelessness
- helplessness
- worthlessness
Case study:
The case study entails Lindsey Vonn who is a ski racer. A range of awards was granted to her. She faced many physical injuries during her career and their psychological impact as well. She has faced depression for a long time. She revealed that her depression was triggered by the following:
- Injuries like ACL tears
- Long recovery periods
- Missing major events (the 2014 Sochi Olympics)

She admitted to living with depression in silence for about a decade. She also used skiing as an escape from her negative thoughts. Her serious injuries, surgeries and nerve damage led to an increased feeling of isolation and sadness. She sought help and used her athlete mindset in recovery. Now retired, she still emphasises emotional well-being and wellness.
Anxiety:
Anxiety is another major part of the psychology of sport injury that players can feel. It is fueled by the following thoughts:
- How long will the healing take?
- Will they ever play the sport again?
- Will I perform the same way or not?
- They might fear missing out on important games or events.
- They may also fear losing their spot on the team.
Anger:
Athletes may feel angry over the entire situation. Anger is created over the unfairness of the whole thing. If you are an athlete, you may ask why me? You could also keep thinking if you could stop it. Doing something differently in the moment is another all-consuming thought. Anger often turns to resentment towards the following:
- Coaches
- Teammates
- Sport
This aspect of the psychology of sport injury can lead to other issues as well.
PTSD:
Athletes can experience injury as a traumatic experience. Some such cases would be if the injury was intensely painful or it had graphic visuals, such as compound fractures. There can also be trauma attached if it occurred in a high-stakes competition. The symptoms can include the following:
- Flashbacks of the injury event.
- Avoiding all aspects traumatic event
- Hyperarousal (i.e. exaggerated startle responses)
- Sleep disturbances
- intrusive thoughts.
For instance, an athlete tears an ACL in a critical game. This part of the psychology of sport injury would lead to an intense fear of the same injury. This is especially visible when they play the next time.
Get useful insights about PTSD Treatment.
Kinesiophobia:
It refers to an intense fear of re-injury. This may happen even after the athlete is completely recovered. This effect is often seen in high-impact sports. For instance, football and gymnastics players can encounter it. The reason for this is the sudden nature of the injury. The severity of the injury is also a reason.
The fear shows in the following ways:
- Hesitation in movements or avoiding certain drills
- Reduced performance due to caution
- Psychological distress before or during games
Disordered Eating
Athletes have specific body composition. Their metabolism and training intensity are also different from other people. Injuries may disrupt them. In a bid to deal with this, the athletes engage in unhealthy eating habits. This effect is common in aesthetic sports. It also appears in weight-related competitions. These include figure skating, ballet, wrestling, etc.. The following negative thoughts fuel this disorder:
- Fear of weight gain during inactivity.
- Pressure to maintain a certain physique or weight class.
- Loss of appetite due to emotional stress.
Substance Misuse
Athletes who are facing an injury and suffering psychologically may turn to addiction. This leads to worsening of mental health in the long run. Some of the drugs that athletes can use are:
- Painkillers
- Alcohol
- Cannabis
- Performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs)
To relieve the emotional or physical pain, they can begin abusing any of those drugs. This drug abuse may develop to permanent dependence unless properly advised.
Post-Athlete depression and identity crisis
After an injury, athletes may get post athlete depression. It also occurs commonly after early retirement. This is a real mental challenge. When an athlete can’t play, they feel a loss of identity. Sport is something that defines their identity. When it is taken away, they may feel sad, anxious, and confused about what’s next. Post-athlete depression needs care and attention.
Psychological Symptoms
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Detachment
- Withdrawal
- Substance abuse
- Self-medicating
- Low self-esteem
- Despair
- Difficulty adjusting to non-sport environments
Mental Strategies Used in the Psychology of Sport Injury
Psychological approaches to sports injury rehabilitation are helpful in making athletes feel relaxed. Therapies help athletes deal with emotions. It also assists them in rebuilding their confidence. Some of the commonly used therapy approaches are as follows:
1. Psychotherapy
Among the talk therapies, psychotherapy or CBT is one of the most common ones. In this, your therapist helps you change your way of thinking. For athletes, it helps them manage their thoughts. A therapist talks to them. They help the athletes spot negative thoughts. After this, they turn these thoughts into positive ones.
Explore more about What is CBT UK
Why it matters:
Since negative thoughts slow down recovery, CBT is useful since it mitigates those thoughts.
Example:
A common negative thought is I won’t ever get better. After CBT, it can be turned into I am healing every day.

2. Mindfulness and other relevant techniques
Mindfulness is one great approach for athletes. It urges you to focus your awareness on the moment. This process is repeated multiple times to ensure that you are entirely present. These techniques help athletes stay relaxed. They also increase focus. Here are some examples of this kind of therapy.
Examples
Mindfulness:
You stay in the moment by paying attention to breathing.
Muscle relaxation:
In this, you tighten and relax muscles to release tension.
Calming images:
You picture the most relaxing place you can think of. It can be a forest or a beach or anything else.
How it helps
- Stops stress about the past or future.
- Helps with pain and sleep.
- Makes rehab feel easier and more peaceful.
Explore our blog to learn more about psychological therapy
3. Motivational Interviewing (MI)
MI is a type of counselling that helps you deal with a change. It helps you work through mixed feelings and find your own reasons to move ahead. For athletes, it helps them identify their motives to go ahead with rehab. The therapist listens and questions them. Athletes discover what is truly important to them during these questions.
Why it matters:
Injury often makes athletes lose focus. MI helps increase their self-confidence. It also assists them in clarifying their future goals and staying on track.
4. Visualisation and Mental Imagery
This technique is basically a practice of using your imagination to picture your success. For athletes, it is useful in visualising themselves playing and training. They can also picture themselves healing. This process is very helpful in preparing them mentally for their next game.
Why it works:
- The brain treats mental practice like real practice.
- It builds confidence, reduces fear, and helps performance.
- It increases mental strength to deal with nervousness in the game.
5. Group therapy
In group therapy, there is a small group of people with similar issues. They are led by a therapist. In the sessions, everyone shares their feelings and listens to others. In the context of sports injuries, members who have injuries and related mental issues can support each other. This decreases loneliness. Support groups and group therapy provide:
- Validation of feelings
- Shared coping strategies
- Hope and motivation
The Role of Coaches in Mental Recovery
A good coach helps in an athlete’s mental recovery. A coach who gives no support increases stress and fear of the athlete. A good coach can boost motivation and help athletes heal. Considering the psychology of sport injury, their role is crucial. Here are some of the roles coaches can play:
- Process grief, anger, or fear
- Cope with identity loss
- Set realistic recovery goals
- Maintain mental discipline throughout physical rehab
Learn more about sports injury rehabilitation here.
Stages of psychological recovery
The psychology of sport injury states that the recovery process for athletes takes time and involves stages. Each stage involves different emotions. Here is how coaches can help through every one of them:
- Shock and Denial:
This is the first stage. In this, athletes often deny their injury. They might try to push through the pain and avoid dealing with it. This stage can cause delays in accepting the need for rest. Here, coaches can help them understand their injury.
- Anger and Frustration:
As the injury sinks in, athletes can feel upset and angry. They become frustrated because of their inability to play and feel upset. This can lead them to feel weak. Here, coaches can make them focus on healing. This can lower such thoughts.
- Bargaining:
Athletes may start to bargain with themselves or others, trying to find ways to heal faster. They might promise to work harder or make deals in hopes of a quick return. Again, coaches have to walk through the entire healing process. They should explain that there are no shortcuts.

- Acceptance:
Over time, athletes begin to accept reality and focus on small steps to improve. Setting new goals helps them move forward. Another tip is to follow the recovery plan. Coaches can encourage them in these steps.
Role of teammates in the psychology of sport injury
A close team can help ease feelings of isolation. This makes recovery less stressful. Athletes are more likely to stay motivated when they have both coaching and teammate support during the healing process. Teammates can also offer the following for better recovery:
- Emotional support
- Encouragement
- Understanding
How Sports Injury Expert Witnesses Help
A sports injury expert witness can explain the mental side of an injury. They play a vital role in legal cases. They show how the psychological impact of injuries in athletes goes beyond the body. This expert help is key to understanding the full picture of recovery.
These witnesses have detailed knowledge about sports injuries. This includes sports medicine, diagnosis, treatment, etc. They also have experience in looking after such cases. They can explain the cause of injury, its extent and the long-term effects of the injury.
Their insights on the psychology of sport injury are valuable in multiple ways. They create a positive environment where athletes feel safe to express concerns. They explain the entire situation to the court. They also share their expert opinions on the matter. They also provide expert reports that contain their findings.
How can Concise Medico support the psychology of sport injury
The key to recovery is understanding the psychology of sport injury. Athletes require both mental and physical treatment. Emotional stress can slow down recovery. Thus, addressing the mental side of healing is crucial. We at Concise Medico support you throughout your healing journey. We provide you with a wide range of sports therapies. We make sure to cater to all aspects of the psychology of sport injury.
Contact us to seek help for psychology of sport injury




