TABLE OF CONTENT
- Understanding the Role of the GMC UK
- General Medical Council UK Registration: A Step-by-Step Guide
- GMC Duties of a Doctor
- General Medical Council Hearings
- The Importance of GMC Revalidation
- GMC and Medico-Legal Work: Protecting Legal and Medical Standards
- Why GMC UK Matters to Patients
- Using GMC-Registered Doctors for Legal Services
- FAQs
Understanding the Role of the GMC UK
The GMC UK or General Medical Council is a public body that keeps UK medical care safe and ethical for the public. It oversees doctors. This allows patients to receive healthcare from capable and dedicated professionals.
The purpose of the General Medical Council (“GMC”) is to “protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public by ensuring proper standards in the practise of medicine.”
General Medical Council
GMC decides who can be a doctor in the UK and sets practice standards for them. From student to senior consultant, all doctors must meet the rules set by the GMC. The GMC Medical Workforce Report 2025 shows that the UK had 296,182 licensed doctors in 2022. By 2025, that number rose to 328,635. This is an 11% increase in 3 years.
General Medical Council UK Registration: A Step-by-Step Guide
To work as a doctor in the UK, you must have General Medical Council UK registration. Without it, you cannot legally work in any UK hospital or clinic.
Here’s how to get registered:
1. Hold a Recognised Medical Degree
You must have a Primary Medical Qualification (PMQ). In case you’re a global alumnus, you must get this confirmed by EPIC (Electronic Portfolio of International Credentials).
2. Prove Your English Skills
You must show proof of English proficiency. Most doctors submit IELTS or OET scores.
3. Pass the PLAB Test or Equivalent
In case you are trained outside the EEA without recognised postgraduate credentials, you’re not eligible for GMC registration. In that situation you need to take the PLAB test.

4. Provide Proof of Experience
The GMC requires recent experience in medicine. You must also show that you’re fit to practise.
5. Apply Online
Apply using your GMC UK online account. Upload your verified documents. Also, pay the registration fee.
Once approved, you become part of the General Medical Council‘s official medical register.
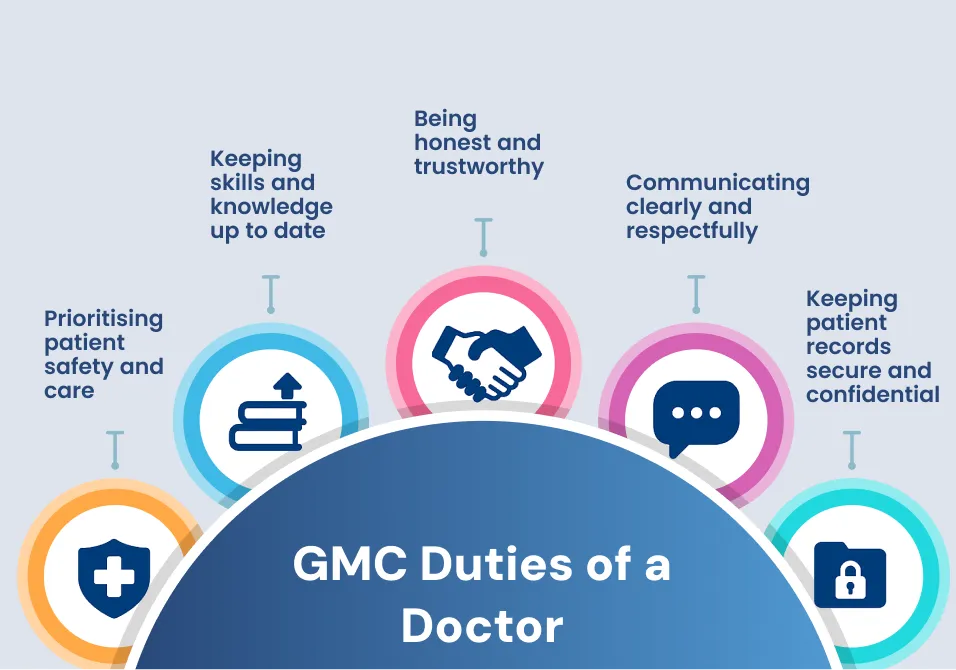
GMC Duties of a Doctor
Ethical and Professional Standards
Doctors must follow the GMC duties of a doctor. These duties are in the “Good Medical Practice” guide.
These duties include:
- Prioritising patient safety and care
- Keeping skills and knowledge up to date
- Being honest and trustworthy
- Communicating clearly and respectfully
- Keeping patient records secure and confidential
Doctors must follow these principles daily. Failing to do so may lead to a General Medical Council hearing, which could affect their licence.
General Medical Council Hearings
When the GMC receives concerns about a doctor’s conduct or skills, it investigates the issue. If the concern is serious, the GMC holds a formal hearing.
What to Expect at a Hearing?
A General Medical Council hearing is about:
- The panel looks at all the important proofs and reports.
- Witnesses and expert speakers give their testimonies in person.
- The panel decides if the doctor can practice safely.
Possible Outcomes
- The panel may issue a formal warning to the doctor.
- The doctor might get a short suspension from practice.
- In severe cases, the doctor might be taken off the register for good.
These hearings keep patients safe and build trust in medical care.
The Importance of GMC Revalidation
Doctors must show they are safe and skilled every five years. This is known as GMC revalidation.
Revalidation involves:
- Annual appraisals
- Feedback from patients and peers
- Proof of ongoing learning and skill development
Doctors who don’t meet the standard may lose their licence. This system helps the GMC ensure only the best stay in practice.
GMC and Medico-Legal Work: Protecting Legal and Medical Standards
Medical professionals often support legal claims. These include:
- Personal injury
Doctors check and record any physical harm a person has suffered. They explain how the personal injury happened and what pain or loss it causes. Their clear reports help courts decide on fair compensation.
- Clinical negligence
Doctors review medical records to see if treatment met the right standards. They point out any mistakes that happened due to clinical negligence and explain how those mistakes led to harm. Their findings guide judgements on whether the treatment was below accepted practice.
Dr Hadiza Bawa-Garba case
In 2015, Dr Hadiza Bawa-Garba faced a manslaughter conviction after a child patient died from misdiagnosis. The GMC struck off her licence for 2 years despite systemic failures. In 2019, the High Court restored her registration highlighting accountability, learning, and patient safety. Her case changed the fitness-to-practice appeals process and professional culture.
- Mental health evaluations
Doctors talk with patients to assess their mood, thoughts and behaviour. They use tests and interviews to diagnose any condition or risk. Their written opinions help courts understand a person’s mental state.
These Medico-legal services rely on doctors for expert evidence.
Here’s how it works:
Medico Legal Reports
Qualified doctors prepare detailed reports. These include:
- Medico legal reports are created by qualified doctors, who know both medicine and law.
- Each report explains the patient’s injuries in clear, simple terms.
- The doctor checks all treatments and medical records. This helps make sure the report is correct.
- The report shows how the injuries could impact the patient’s health and daily life over time.
- It concludes with clinical opinions made for court use.
Expert Testimony
Doctors may also attend court as expert witnesses. They answer questions from lawyers and judges. Their words influence the final legal outcome.
All doctors registered with the General Medical Council must follow strict rules when doing medico-legal work.
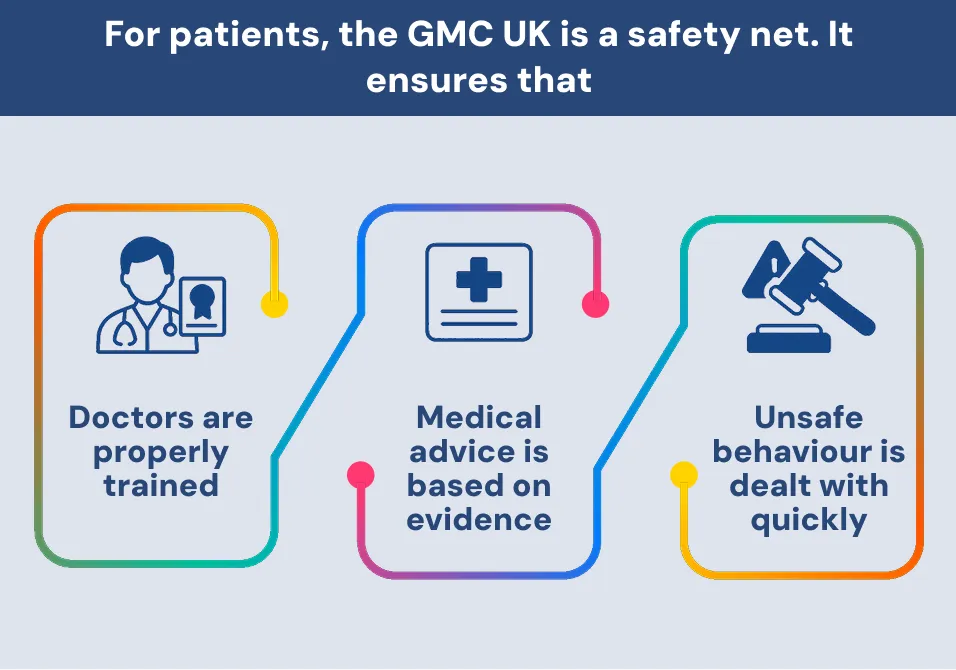
Why GMC UK Matters to Patients
The General Medical Council does more than setting rules. It also builds trust in the UK health system. The General Medical Council UK is the guardian of trust in UK medical services. From guiding doctors to protecting patients, its role is vital. Whether you’re a patient, lawyer, or healthcare provider, knowing the rules of the GMC UK helps you make informed choices.
For patients, the GMC UK is a safety net. It ensures that:
- Doctors are properly trained
- Medical advice is based on evidence
- Unsafe behaviour is dealt with quickly
Doctors must meet high ethical, legal, and clinical standards. Those who don’t, may face a General Medical Council hearing. If you need expert medical evidence, always ask if the doctor is GMC UK registered.
Using GMC-Registered Doctors for Legal Services
If you need medico-legal help, like a report or expert opinion, go with GMC-registered professionals. They follow clear standards. They ensure:
- Evidence is reliable
- Reports are clear and unbiased
- Testimony is based on verified facts
At Concise Medico, we work only with doctors who are fully GMC UK certified. This keeps our services trusted and court-ready.
FAQs
Understanding the Role of the GMC UK
The GMC UK or General Medical Council is a public body that keeps UK medical care safe and ethical for the public. It oversees doctors. This allows patients to receive healthcare from capable and dedicated professionals.
The purpose of the General Medical Council (“GMC”) is to “protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public by ensuring proper standards in the practise of medicine.”
General Medical Council
GMC decides who can be a doctor in the UK and sets practice standards for them. From student to senior consultant, all doctors must meet the rules set by the GMC. The GMC Medical Workforce Report 2025 shows that the UK had 296,182 licensed doctors in 2022. By 2025, that number rose to 328,635. This is an 11% increase in 3 years.
General Medical Council UK Registration: A Step-by-Step Guide
To work as a doctor in the UK, you must have General Medical Council UK registration. Without it, you cannot legally work in any UK hospital or clinic.
Here’s how to get registered:
1. Hold a Recognised Medical Degree
You must have a Primary Medical Qualification (PMQ). In case you’re a global alumnus, you must get this confirmed by EPIC (Electronic Portfolio of International Credentials).
2. Prove Your English Skills
You must show proof of English proficiency. Most doctors submit IELTS or OET scores.
3. Pass the PLAB Test or Equivalent
In case you are trained outside the EEA without recognised postgraduate credentials, you’re not eligible for GMC registration. In that situation you need to take the PLAB test.

4. Provide Proof of Experience
The GMC requires recent experience in medicine. You must also show that you’re fit to practise.
5. Apply Online
Apply using your GMC UK online account. Upload your verified documents. Also, pay the registration fee.
Once approved, you become part of the General Medical Council‘s official medical register.
GMC Duties of a Doctor
Ethical and Professional Standards
Doctors must follow the GMC duties of a doctor. These duties are in the “Good Medical Practice” guide.
These duties include:
- Prioritising patient safety and care
- Keeping skills and knowledge up to date
- Being honest and trustworthy
- Communicating clearly and respectfully
- Keeping patient records secure and confidential
Doctors must follow these principles daily. Failing to do so may lead to a General Medical Council hearing, which could affect their licence.

General Medical Council Hearings
When the GMC receives concerns about a doctor’s conduct or skills, it investigates the issue. If the concern is serious, the GMC holds a formal hearing.
What to Expect at a Hearing?
A General Medical Council hearing is about:
- The panel looks at all the important proofs and reports.
- Witnesses and expert speakers give their testimonies in person.
- The panel decides if the doctor can practice safely.
Possible Outcomes
- The panel may issue a formal warning to the doctor.
- The doctor might get a short suspension from practice.
- In severe cases, the doctor might be taken off the register for good.
These hearings keep patients safe and build trust in medical care.
The Importance of GMC Revalidation
Doctors must show they are safe and skilled every five years. This is known as GMC revalidation.
Revalidation involves:
- Annual appraisals
- Feedback from patients and peers
- Proof of ongoing learning and skill development
Doctors who don’t meet the standard may lose their licence. This system helps the GMC ensure only the best stay in practice.
GMC and Medico-Legal Work: Protecting Legal and Medical Standards
Medical professionals often support legal claims. These include:
- Personal injury
Doctors check and record any physical harm a person has suffered. They explain how the personal injury happened and what pain or loss it causes. Their clear reports help courts decide on fair compensation.
- Clinical negligence
Doctors review medical records to see if treatment met the right standards. They point out any mistakes that happened due to clinical negligence and explain how those mistakes led to harm. Their findings guide judgements on whether the treatment was below accepted practice.
Dr Hadiza Bawa-Garba case
In 2015, Dr Hadiza Bawa-Garba faced a manslaughter conviction after a child patient died from misdiagnosis. The GMC struck off her licence for 2 years despite systemic failures. In 2019, the High Court restored her registration highlighting accountability, learning, and patient safety. Her case changed the fitness-to-practice appeals process and professional culture.
- Mental health evaluations
Doctors talk with patients to assess their mood, thoughts and behaviour. They use tests and interviews to diagnose any condition or risk. Their written opinions help courts understand a person’s mental state.
These Medico-legal services rely on doctors for expert evidence.
Here’s how it works:
Medico Legal Reports
Qualified doctors prepare detailed reports. These include:
- Medico legal reports are created by qualified doctors, who know both medicine and law.
- Each report explains the patient’s injuries in clear, simple terms.
- The doctor checks all treatments and medical records. This helps make sure the report is correct.
- The report shows how the injuries could impact the patient’s health and daily life over time.
- It concludes with clinical opinions made for court use.
Expert Testimony
Doctors may also attend court as expert witnesses. They answer questions from lawyers and judges. Their words influence the final legal outcome.
All doctors registered with the General Medical Council must follow strict rules when doing medico-legal work.
Why GMC UK Matters to Patients
The General Medical Council does more than setting rules. It also builds trust in the UK health system. The General Medical Council UK is the guardian of trust in UK medical services. From guiding doctors to protecting patients, its role is vital. Whether you’re a patient, lawyer, or healthcare provider, knowing the rules of the GMC UK helps you make informed choices.
For patients, the GMC UK is a safety net. It ensures that:
- Doctors are properly trained
- Medical advice is based on evidence
- Unsafe behaviour is dealt with quickly
Doctors must meet high ethical, legal, and clinical standards. Those who don’t, may face a General Medical Council hearing. If you need expert medical evidence, always ask if the doctor is GMC UK registered.

Using GMC-Registered Doctors for Legal Services
If you need medico-legal help, like a report or expert opinion, go with GMC-registered professionals. They follow clear standards. They ensure:
- Evidence is reliable
- Reports are clear and unbiased
- Testimony is based on verified facts
At Concise Medico, we work only with doctors who are fully GMC UK certified. This keeps our services trusted and court-ready.