TABLE OF CONTENT
Ultrasound is commonly used as an early scan in cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Doctors use it to look at lumps organs and abnormal changes before deciding if further tests are needed.
One of the common concerns is ‘can cancer be found in ultrasound’. Well, in some cases, it can detect changes that may suggest cancer. But it usually cannot confirm cancer without further tests.
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to detect tumours inside the body. The waves travel through tissue and bounce back in different ways. It helps create an image of what is happening inside your body.
Ultrasound is sometimes seen as a basic test compared with MRI or CT scans. It can still help find suspicious changes that need follow up testing. Some studies report accuracy ranges around 80.1% to 93.9% for specific uses of ultrasound.
This blog explains where ultrasound helps in cancer diagnosis and monitoring and where other tests are still needed.
What Is Ultrasound
Ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to create images of structures inside the body.
A transducer sends sound waves into the body and the echoes return to create live images on a screen in real time.
Ultrasound is often used in healthcare because it is:
- Free from ionising radiation
- Safe for repeated use
- Quick and commonly available in outpatient settings
- Able to show movement and blood flow in real time
Ultrasound is safe and fast. That’s why doctors often use ultrasound as a first test when cancer is suspected.
Why Is Ultrasound Important In Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis is one of the most serious medical processes. If it goes wrong, it can have serious consequences. Ultrasound supports cancer assessment in several practical ways.
It helps doctors:
- Look for abnormal masses or swelling
- Check whether a lump is solid or fluid filled
- Check the size and shape of organs
- Detect blood flow patterns that may look unusual
- Decide if more tests are needed
Ultrasound can detect many abnormal findings, but it often needs follow up tests to confirm what the change means.
Can Cancer Be Found In Ultrasound
In some cases, ultrasound can detect changes that may suggest cancer. But it usually cannot confirm cancer without further tests.
Ultrasound can:
- Detect lumps or masses
- Show irregular borders or distorted tissue
- Show areas with unusual blood flow
- Help track whether a lump changes over time
However, ultrasound cannot:
- Confirm cancer on its own
- Replace biopsy and lab testing
- Detect every cancer, especially those deep in the body or behind air or bone
Ultrasound is most useful for highlighting a concern early. This can lead to a biopsy, CT scan, MRI or specialist referral.
Case Study: Cancer Diagnosis
This is a real case from a medical report where breast cancer was spread to the thyroid.
Patient Background
The patient was a 46 years old woman with a history of breast cancer. It developed swelling in her neck. The patient was then sent for a thyroid ultrasound.
Ultrasound Findings
- The scan showed thyroid enlargement and unusual changes.
- It was first thought to be thyroiditis.
- Cytology and histopathology later confirmed the changes were metastatic breast cancer cells.
Role of Ultrasound
Ultrasound helped spot the abnormal pattern early. It guided the needle during biopsy and showed the need for further tests.
Outcome
The correct diagnosis allowed timely treatment. The follow up ultrasounds were used to monitor the lesion during recovery.
Types of Ultrasound Used In Cancer Assessment
Ultrasound may be done externally or internally. Following are the two types of ultrasound used in cancer assessment.
External ultrasound: A probe is moved over the skin.
Internal ultrasound: A probe is placed inside the body, such as in the vagina or the rectum.
Ultrasound works best for soft tissues and many internal organs. Due to its versatility, it is used in several cancer assessments.
Types of Cancers Assessed With Ultrasound
Following are the types of cancers commonly assessed with ultrasound.
1. Breast Cancer
Ultrasound is commonly used in breast assessment, especially when:
- A lump can be felt during an exam
- Breast tissue is dense
- A mammogram result is unclear
Ultrasound can help:
- To tell the difference between cysts and solid lumps
- To assess the shape and edges of a lump
- To identify areas that may need a biopsy
- To guide needles safely during sampling
2. Liver Cancer
The liver is a soft internal organ, so ultrasound is often used early in liver assessment. It can help by:
- Detecting suspicious lesions in the liver
- Checking liver size and structure
- Monitoring people with long term liver disease
- Supporting earlier detection in higher risk patients
Because ultrasound is safe, it can be repeated when ongoing checks are needed.
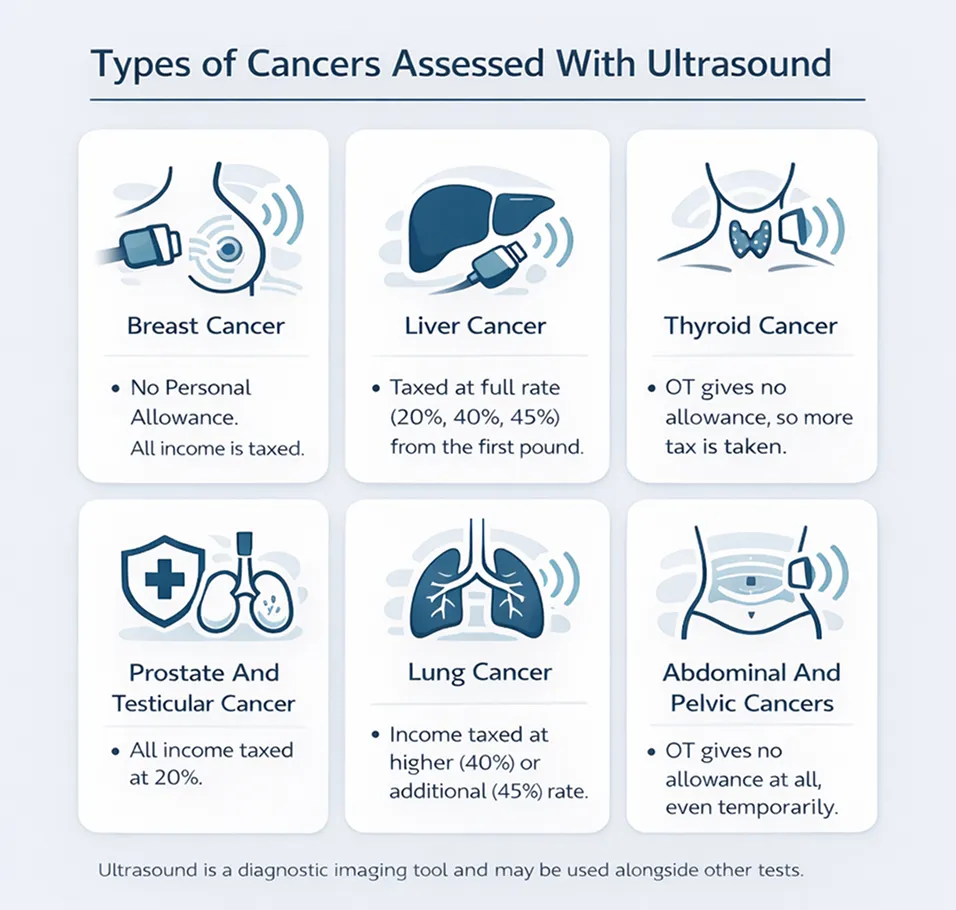
3. Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid lumps are common and most are not cancerous. Ultrasound helps doctors assess features such as:
- Irregular or rough edges
- Tiny calcium spots
- Increased blood flow in a nodule
- One side looking different from the other
This helps reduce unnecessary worry while still identifying nodules that need further investigation.
4. Prostate And Testicular Cancer
Ultrasound can support assessment in men by helping doctors:
- Find suspicious areas
- Measure the size of a suspected tumour
- Guide biopsy needles accurately
- Reduce risk to nearby tissue
Live imaging helps improve accuracy during procedures.
5. Lung Cancer
CT is more common for lung cancer diagnosis, but ultrasound can still help in specific situations, such as:
- Detecting fluid around the lungs
- Assessing tumours close to the chest wall
- Supporting biopsy guidance in selected cases
- Checking complications
Ultrasound cannot see well through air. It cannot assess the deeper parts of the lungs in the same way as CT. That’s why CT is more commonly used by doctors for lung cancer diagnosis.
6. Abdominal And Pelvic Cancers
Ultrasound is commonly used to assess the abdomen and pelvis when cancer is suspected. It may be used to check for findings linked to:
- Kidney cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Uterine cancer
- Bladder tumours
- Pancreatic problems
Special internal scans such as transvaginal ultrasound and transrectal ultrasound can provide clearer images in specific areas.
Telling Cancer Apart From Other Problems
Not every lump means cancer. Ultrasound can help show when a lump is more likely to be something else, such as a cyst or a benign swelling.
This supports safer decisions and can help avoid unnecessary tests.
A good example is hernia diagnosis with ultrasound. With ultrasound doctors can:
- Watch muscles move.
- See tissue pushing through muscle.
- Clearly confirm a hernia.
- Avoid mixing it up with cancer.
Proper hernia diagnosis with ultrasound saves people from stress and unnecessary tests.
Ultrasound Guided Biopsy In Cancer Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis, doctors often need a biopsy. Ultrasound helps during biopsy by:
- Showing the needle movement in real time
- Helping target the right area
- Reducing risks during sampling
- Improving the chance of getting a useful sample
Because ultrasound uses no ionising radiation, it is suitable for guidance during procedures.
Monitoring Cancer After Diagnosis
Cancer care continues after diagnosis. Ultrasound can be used in monitoring to:
- Measure tumour size
- Check response to treatment
- Look for signs of recurrence in some cases
- Detect problems such as fluid build up
This makes ultrasound useful for follow up in selected cancers and situations.
Benefits And Limitations Of Ultrasound In Cancer Diagnosis
Ultrasound is widely used, but it is not perfect. It has clear strengths and clear limits.
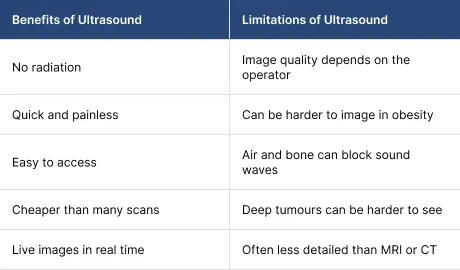
These strengths are why ultrasound is common in early assessment. Doctors usually combine it with other tests when they need a definite diagnosis.
A misdiagnosis can be catastrophic so it’s important to get it right. If you suspect a misdiagnosis you should check out our blog on what you should do if you suspect a cancer misdiagnosis.
Ultrasound In Cancer Diagnosis: The Future
Ultrasound remains useful and continues to improve with new technology. Developments that can support cancer assessment include:
- Contrast enhanced ultrasound
- Elastography, which checks tissue stiffness
- Improved blood flow imaging
These advances can help ultrasound provide more detail in certain clinical situations.
Conclusion
Ultrasound plays a key role in cancer diagnosis and monitoring. It can:
- Give early indication of suspicious changes
- Offer a safe option without ionising radiation
- Help tell a cyst from a solid lump
- Support biopsy guidance
- Provide fast, real time imaging
Concise Medico understands that cancer diagnosis is an important part of the medical process. A misdiagnosis can be disastrous and result in ruin. In order to make sure it never happens you need the right diagnosis techniques and services. Contact us now to get the best in diagnostic services.
FAQs
Ultrasound is commonly used as an early scan in cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Doctors use it to look at lumps organs and abnormal changes before deciding if further tests are needed.
One of the common concerns is ‘can cancer be found in ultrasound’. Well, in some cases, it can detect changes that may suggest cancer. But it usually cannot confirm cancer without further tests.
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to detect tumours inside the body. The waves travel through tissue and bounce back in different ways. It helps create an image of what is happening inside your body.
Ultrasound is sometimes seen as a basic test compared with MRI or CT scans. It can still help find suspicious changes that need follow up testing. Some studies report accuracy ranges around 80.1% to 93.9% for specific uses of ultrasound.
This blog explains where ultrasound helps in cancer diagnosis and monitoring and where other tests are still needed.
What Is Ultrasound
Ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses high frequency sound waves to create images of structures inside the body.
A transducer sends sound waves into the body and the echoes return to create live images on a screen in real time.
Ultrasound is often used in healthcare because it is:
- Free from ionising radiation
- Safe for repeated use
- Quick and commonly available in outpatient settings
- Able to show movement and blood flow in real time
Ultrasound is safe and fast. That’s why doctors often use ultrasound as a first test when cancer is suspected.
Why Is Ultrasound Important In Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis is one of the most serious medical processes. If it goes wrong, it can have serious consequences. Ultrasound supports cancer assessment in several practical ways.
It helps doctors:
- Look for abnormal masses or swelling
- Check whether a lump is solid or fluid filled
- Check the size and shape of organs
- Detect blood flow patterns that may look unusual
- Decide if more tests are needed
Ultrasound can detect many abnormal findings, but it often needs follow up tests to confirm what the change means.
Can Cancer Be Found In Ultrasound
In some cases, ultrasound can detect changes that may suggest cancer. But it usually cannot confirm cancer without further tests.
Ultrasound can:
- Detect lumps or masses
- Show irregular borders or distorted tissue
- Show areas with unusual blood flow
- Help track whether a lump changes over time
However, ultrasound cannot:
- Confirm cancer on its own
- Replace biopsy and lab testing
- Detect every cancer, especially those deep in the body or behind air or bone
Ultrasound is most useful for highlighting a concern early. This can lead to a biopsy, CT scan, MRI or specialist referral.
Case Study: Cancer Diagnosis
This is a real case from a medical report where breast cancer was spread to the thyroid.
Patient Background
The patient was a 46 years old woman with a history of breast cancer. It developed swelling in her neck. The patient was then sent for a thyroid ultrasound.
Ultrasound Findings
- The scan showed thyroid enlargement and unusual changes.
- It was first thought to be thyroiditis.
- Cytology and histopathology later confirmed the changes were metastatic breast cancer cells.
Role of Ultrasound
Ultrasound helped spot the abnormal pattern early. It guided the needle during biopsy and showed the need for further tests.
Outcome
The correct diagnosis allowed timely treatment. The follow up ultrasounds were used to monitor the lesion during recovery.
Types of Ultrasound Used In Cancer Assessment
Ultrasound may be done externally or internally. Following are the two types of ultrasound used in cancer assessment.
External ultrasound: A probe is moved over the skin.
Internal ultrasound: A probe is placed inside the body, such as in the vagina or the rectum.
Ultrasound works best for soft tissues and many internal organs. Due to its versatility, it is used in several cancer assessments.
Types of Cancers Assessed With Ultrasound
Following are the types of cancers commonly assessed with ultrasound.
1. Breast Cancer
Ultrasound is commonly used in breast assessment, especially when:
- A lump can be felt during an exam
- Breast tissue is dense
- A mammogram result is unclear
Ultrasound can help:
- To tell the difference between cysts and solid lumps
- To assess the shape and edges of a lump
- To identify areas that may need a biopsy
- To guide needles safely during sampling
2. Liver Cancer
The liver is a soft internal organ, so ultrasound is often used early in liver assessment. It can help by:
- Detecting suspicious lesions in the liver
- Checking liver size and structure
- Monitoring people with long term liver disease
- Supporting earlier detection in higher risk patients
Because ultrasound is safe, it can be repeated when ongoing checks are needed.

3. Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid lumps are common and most are not cancerous. Ultrasound helps doctors assess features such as:
- Irregular or rough edges
- Tiny calcium spots
- Increased blood flow in a nodule
- One side looking different from the other
This helps reduce unnecessary worry while still identifying nodules that need further investigation.
4. Prostate And Testicular Cancer
Ultrasound can support assessment in men by helping doctors:
- Find suspicious areas
- Measure the size of a suspected tumour
- Guide biopsy needles accurately
- Reduce risk to nearby tissue
Live imaging helps improve accuracy during procedures.
5. Lung Cancer
CT is more common for lung cancer diagnosis, but ultrasound can still help in specific situations, such as:
- Detecting fluid around the lungs
- Assessing tumours close to the chest wall
- Supporting biopsy guidance in selected cases
- Checking complications
Ultrasound cannot see well through air. It cannot assess the deeper parts of the lungs in the same way as CT. That’s why CT is more commonly used by doctors for lung cancer diagnosis.
6. Abdominal And Pelvic Cancers
Ultrasound is commonly used to assess the abdomen and pelvis when cancer is suspected. It may be used to check for findings linked to:
- Kidney cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Uterine cancer
- Bladder tumours
- Pancreatic problems
Special internal scans such as transvaginal ultrasound and transrectal ultrasound can provide clearer images in specific areas.
Telling Cancer Apart From Other Problems
Not every lump means cancer. Ultrasound can help show when a lump is more likely to be something else, such as a cyst or a benign swelling.
This supports safer decisions and can help avoid unnecessary tests.
A good example is hernia diagnosis with ultrasound. With ultrasound doctors can:
- Watch muscles move.
- See tissue pushing through muscle.
- Clearly confirm a hernia.
- Avoid mixing it up with cancer.
Proper hernia diagnosis with ultrasound saves people from stress and unnecessary tests.
Ultrasound Guided Biopsy In Cancer Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis, doctors often need a biopsy. Ultrasound helps during biopsy by:
- Showing the needle movement in real time
- Helping target the right area
- Reducing risks during sampling
- Improving the chance of getting a useful sample
Because ultrasound uses no ionising radiation, it is suitable for guidance during procedures.
Monitoring Cancer After Diagnosis
Cancer care continues after diagnosis. Ultrasound can be used in monitoring to:
- Measure tumour size
- Check response to treatment
- Look for signs of recurrence in some cases
- Detect problems such as fluid build up
This makes ultrasound useful for follow up in selected cancers and situations.
Benefits And Limitations Of Ultrasound In Cancer Diagnosis
Ultrasound is widely used, but it is not perfect. It has clear strengths and clear limits.

These strengths are why ultrasound is common in early assessment. Doctors usually combine it with other tests when they need a definite diagnosis.
A misdiagnosis can be catastrophic so it’s important to get it right. If you suspect a misdiagnosis you should check out our blog on what you should do if you suspect a cancer misdiagnosis.
Ultrasound In Cancer Diagnosis: The Future
Ultrasound remains useful and continues to improve with new technology. Developments that can support cancer assessment include:
- Contrast enhanced ultrasound
- Elastography, which checks tissue stiffness
- Improved blood flow imaging
These advances can help ultrasound provide more detail in certain clinical situations.
Conclusion
Ultrasound plays a key role in cancer diagnosis and monitoring. It can:
- Give early indication of suspicious changes
- Offer a safe option without ionising radiation
- Help tell a cyst from a solid lump
- Support biopsy guidance
- Provide fast, real time imaging
Concise Medico understands that cancer diagnosis is an important part of the medical process. A misdiagnosis can be disastrous and result in ruin. In order to make sure it never happens you need the right diagnosis techniques and services. Contact us now to get the best in diagnostic services.




