TABLE OF CONTENT
- What is an X Ray Scan
- Types of of X‑Ray Scan
- Application of X‑Ray in Medicine and Law
- Medicolegal X‑rays as Evidence in Court
- Key Benefits of X‑Ray Imaging in Legal Proceedings
- Limitations of X-Ray Evidence
- Safety and Hazards
- Cost and Accessibility in the UK
- The Critical Role of X‑Ray Scans in Legal and Medical Contexts
- FAQs
In many legal cases involving physical harm, clinical imaging is essential for verifying the presence and extent of injury. Among the imaging tools frequently requested by legal and medical experts is the X-ray scan. It is valued because one of the applications of X-ray is to provide objective and detailed evidence. Courts and legal teams rely on these medical images to assess the nature and extent of physical harm. The clarity and speed of the x-ray, allow experts to verify claims, detect inconsistencies, and build stronger arguments based on visual proof. This makes x-ray evidence crucial in both civil and criminal proceedings where physical injury is in question.
What is an X Ray Scan
In x-ray scan a machine sends a small burst of radiation through your body and onto a detector. Bones block more radiation and show up white. Muscles and organs let more radiation through and look gray. Doctors use the resulting picture to spot broken bones, joint problems or other issues.
Types of of X‑Ray Scan
Many types of scans are used to capture images of different organs. Below are the main scan types:
Radiography
Radiography is the classic type of x rays method for bones and chest images. It makes flat, 2D pictures. Radiographs find fractures, pneumonia, and arthritis.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy gives live, moving X‑ray images. It helps guide tests like barium swallows. Regular scans can spot shifts inside the body.
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography (CT) combines X‑rays and computer work to make 3D cross sections. CT scans spot tumours, complex breaks, and bleeding. They give more detail but use more radiation.
“Computerised tomography (CT) is not generally used for assessment of the hip and groin, due to MRI being able to give a more complete picture and also to the radiation dose involved, specifically to the gonad region of young adolescents and adults involved in professional sport.”
Amanda Parry
Mammography
Mammography uses low‑dose X‑rays for breast checks and early cancer signs. It can show tiny calcifications before lumps form. Regular mammograms save lives by finding cancer early.
Application of X‑Ray in Medicine and Law
The importance of X-ray scans in legal proceedings is as important as it is in the field of medicine. Here are the uses of X-rays in health and law:
1. Medical Applications of X‑Ray
Medical uses of x rays include:
Orthopaedic Imaging
X‑ray scans reveal fractures, dislocations, and arthritis with clear detail. Doctors use these images to plan surgery. They also guide rehab exercises.
Thoracic Imaging
Chest X‑rays detect pneumonia, collapsed lungs, and heart size changes. Quick scans let doctors start treatment fast. This enhances patient recovery.
Abdominal Imaging
Abdominal X‑rays show blockages, kidney stones, and ingested foreign bodies. They help emergency teams make life‑saving decisions.
Paediatric Imaging
X‑ray protocols for children use low doses to protect growing bones. Follow‑up images track healing as kids recover.
2. Legal Application of X‑Ray
X-ray scans play a key role in legal cases, due to their great legal value. These are the legal uses of X-rays:
Medico‑Legal Reporting
An X-ray scan provides clear, time-stamped images for legal medical reports. Radiologists review these scans and explain findings in court as expert witnesses. This solid visual proof strengthens legal arguments.
Personal Injury Evidence
An X-ray scan shows exactly where injuries lie and how severe they are. In injury claims, lawyers use these images to link harm to an event and to set fair compensation. Like, after a car crash, X-ray scans can reveal broken bones or tissue damage that match the accident’s force.
Malpractice case (1965)
In Darling, a young man arrived with a severely injured leg, but the hospital failed to perform the proper X-ray scan before setting his bone. The delayed and missed imaging led to permanent damage. The Court held the hospital strictly liable, stressing that a timely, correctly interpreted X-ray scan is a basic standard of care. This decision underscores how missing or misreading an x-ray can have serious legal consequences.
Forensic Imaging
Forensic imaging means using X‑ray scans in legal cases. These scans can show old, healed breaks or bits of metal left inside the body. By studying the X‑rays, specialists can work out when the injury happened and help the court understand the full story.
Criminal Cases
An X-ray scan can spot bullets, sharp objects, or other items inside the body. Police and doctors use these pictures to see entry and exit points of a shot or stab. This clear view helps prove how a crime happened and supports evidence in court.
Insurance Claims
An X-ray scan shows insurers the true extent of an injury. This proof removes doubt and speeds up claim decisions. Accurate images help ensure fair payouts for medical costs.
Medicolegal X‑rays as Evidence in Court
In injury or negligence cases, experts use X-ray as evidence in court. It takes clear pictures of injuries and saves them as records. This makes x-ray scans strong proof to support legal claims. They:
- Show injury type and location.
- Date the injury by healing stages.
- Prove or disprove claims of harm.
Impact on Judgments
X‑ray in court can help a judge or jury by showing injuries in clear detail. In 2024, the NHS paid private firms a record £216 million to report X-rays and scans because hospitals faced a 30 percent radiologist shortfall. This gap risks delaying important X-ray reports needed for legal cases. Which can slow evidence gathering and affect court decisions Such delays underscore just how vital timely X-ray evidence is for achieving fair and accurate legal outcome.
Expert Testimony and Reports
Radiologists don’t just supply scan images. They write detailed reports that tie findings to medical standards. In court, they explain how an injury occurred and its severity in simple words. Their testimony adds weight and guides judges.
Digital Preservation and Access
Unlike memories, digital X‑rays stay unchanged in (PACS) picture archiving communication systems. These systems keep a clear chain of custody. This permanence makes X-ray in court evidence hard to dispute. Images and reports stay intact through appeals and reviews. Easy access means evidence can be shown even years later.
Key Benefits of X‑Ray Imaging in Legal Proceedings
By far, it is clear that X-rays have a vital role in legal proceedings. Below are the key benefits of X-ray scans and reports, when presented in courts:
Speedy Evidence Gathering
An X-ray scan delivers clear images in minutes, so legal teams receive evidence quickly. Quick scans help set a clear timeline and guide court actions.
Visual Documentation of Injuries
An X-ray scan highlights bones and soft tissue in high contrast. In injury claims or accident cases, these images show breaks or hidden damage without guesswork. Judges and juries use this proof to determine liability and award fair compensation.
Patient Comfort and Compliance
An X-ray scan is painless and needs no cuts or needles. You stay still for only a few seconds while the scan is being conducted. This ease helps clients, witnesses, or claimants finish the test, even after trauma, ensuring reliable evidence.
Easy Access and Record Keeping
Most clinics and hospitals offer an X-ray scan, so there’s little wait for both NHS and private care. The images feed directly into medical records, ready to attach to legal files as court exhibits.
Want to know which scan is better?
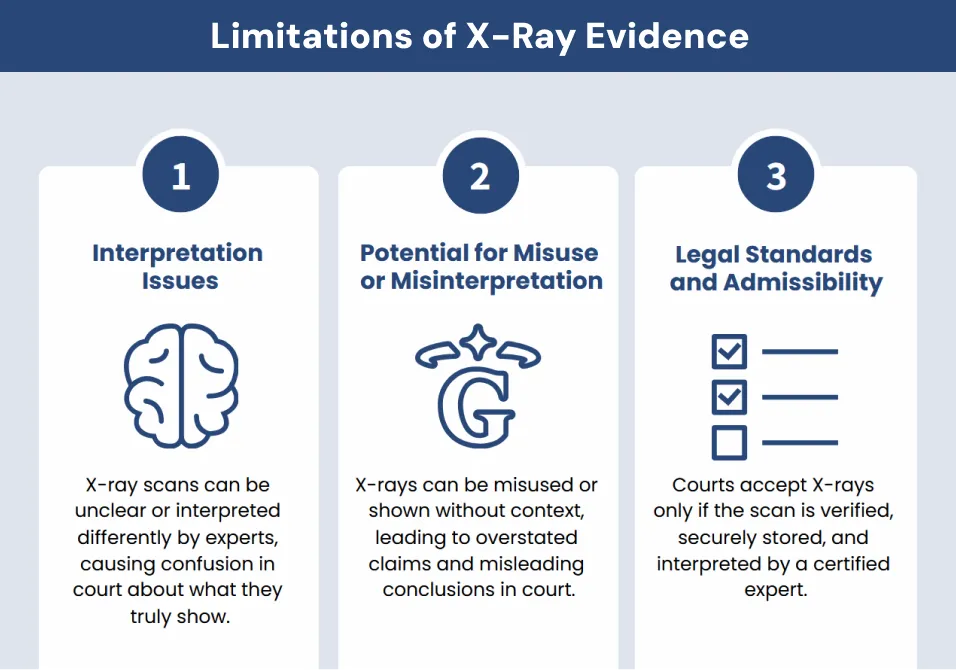
Limitations of X-Ray Evidence
Interpretation Issues
X-ray images can sometimes be hard to read if the scan is blurry or the body parts overlap. Different experts might give different opinions on the same image. This can lead to confusion in court about what the scan really shows.
Potential for Misuse or Misinterpretation
An X-ray scan can be taken out of context or shown without the full medical story. Lawyers or witnesses might overstate what the image proves. This risks leading judges or juries to the wrong conclusion.
Legal Standards and Admissibility
Courts only accept an X-ray scan if it follows clear rules. These include proof that the machine was checked and the scan kept safe from tampering. Lawyers also must show that the person reading the scan is a certified expert with the right training.
Safety and Hazards
Below is an overview of the main risks and safety measures for X-ray use:
X‑Ray Hazards
X‑rays use ionising radiation that can harm cells and DNA over time. Technicians follow ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) rules to keep doses low. Shields and limits protect patients and staff.
Why Are X‑Rays Harmful
High dose X-rays or repeat scans may raise cancer risk, especially in kids. Pregnant women must avoid scans unless essential. Modern digital systems cut doses by up to 60 percent compared to old machines.
Reducing Radiation Risk
To avoid risk wear lead aprons and thyroid collars. Use collimators to narrow the beam. Strict scheduling avoids repeat scans. Regular maintenance and dose checks ensure safe use.
Cost and Accessibility in the UK
Here’s a quick look at X-ray prices and how to access scans in the UK:
Private X‑Ray Services
A private X‑ray often has shorter wait times and flexible hours. Clinics offer digital or portable scans, even on weekends. Fast service helps legal teams meet deadlines and supports urgent care.
Cost of X‑Ray UK
The cost of X-ray in the UK varies by provider. NHS scans are free with referral. Private scans range from £50 to £200 per view. Always check your insurer’s cover to avoid surprise bills.
The Critical Role of X‑Ray Scans in Legal and Medical Contexts
The X-ray scans remain essential to health care and justice. These images provide clear, objective evidence for both clinical diagnoses and courtroom proceedings. These scans give clear proof of any injury or a disease. Knowing why X-rays are harmful, the advantages of an X-ray, and the cost of X-ray in the UK helps you choose wisely. Whether via the NHS or private X‑ray, safe, reliable imaging supports both treatment and justice.
Schedule your next X-ray scan with Concise Medico for fast, expert imaging and medico‑legal support.
Contact us for expert consultation services and detailed medico‑legal X‑ray reports.
FAQs
In many legal cases involving physical harm, clinical imaging is essential for verifying the presence and extent of injury. Among the imaging tools frequently requested by legal and medical experts is the X-ray scan. It is valued because one of the applications of X-ray is to provide objective and detailed evidence. Courts and legal teams rely on these medical images to assess the nature and extent of physical harm. The clarity and speed of the x-ray, allow experts to verify claims, detect inconsistencies, and build stronger arguments based on visual proof. This makes x-ray evidence crucial in both civil and criminal proceedings where physical injury is in question.
What is an X Ray Scan
In x-ray scan a machine sends a small burst of radiation through your body and onto a detector. Bones block more radiation and show up white. Muscles and organs let more radiation through and look gray. Doctors use the resulting picture to spot broken bones, joint problems or other issues.
Types of of X‑Ray Scan
Many types of scans are used to capture images of different organs. Below are the main scan types:
Radiography
Radiography is the classic type of x rays method for bones and chest images. It makes flat, 2D pictures. Radiographs find fractures, pneumonia, and arthritis.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy gives live, moving X‑ray images. It helps guide tests like barium swallows. Regular scans can spot shifts inside the body.
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography (CT) combines X‑rays and computer work to make 3D cross sections. CT scans spot tumours, complex breaks, and bleeding. They give more detail but use more radiation.

“Computerised tomography (CT) is not generally used for assessment of the hip and groin, due to MRI being able to give a more complete picture and also to the radiation dose involved, specifically to the gonad region of young adolescents and adults involved in professional sport.”
Amanda Parry
Mammography
Mammography uses low‑dose X‑rays for breast checks and early cancer signs. It can show tiny calcifications before lumps form. Regular mammograms save lives by finding cancer early.
Application of X‑Ray in Medicine and Law
The importance of X-ray scans in legal proceedings is as important as it is in the field of medicine. Here are the uses of X-rays in health and law:
1. Medical Applications of X‑Ray
Medical uses of x rays include:
Orthopaedic Imaging
X‑ray scans reveal fractures, dislocations, and arthritis with clear detail. Doctors use these images to plan surgery. They also guide rehab exercises.
Thoracic Imaging
Chest X‑rays detect pneumonia, collapsed lungs, and heart size changes. Quick scans let doctors start treatment fast. This enhances patient recovery.
Abdominal Imaging
Abdominal X‑rays show blockages, kidney stones, and ingested foreign bodies. They help emergency teams make life‑saving decisions.

Paediatric Imaging
X‑ray protocols for children use low doses to protect growing bones. Follow‑up images track healing as kids recover.
2. Legal Application of X‑Ray
X-ray scans play a key role in legal cases, due to their great legal value. These are the legal uses of X-rays:
Medico‑Legal Reporting
An X-ray scan provides clear, time-stamped images for legal medical reports. Radiologists review these scans and explain findings in court as expert witnesses. This solid visual proof strengthens legal arguments.
Personal Injury Evidence
An X-ray scan shows exactly where injuries lie and how severe they are. In injury claims, lawyers use these images to link harm to an event and to set fair compensation. Like, after a car crash, X-ray scans can reveal broken bones or tissue damage that match the accident’s force.
Malpractice case (1965)
In Darling, a young man arrived with a severely injured leg, but the hospital failed to perform the proper X-ray scan before setting his bone. The delayed and missed imaging led to permanent damage. The Court held the hospital strictly liable, stressing that a timely, correctly interpreted X-ray scan is a basic standard of care. This decision underscores how missing or misreading an x-ray can have serious legal consequences.

Forensic Imaging
Forensic imaging means using X‑ray scans in legal cases. These scans can show old, healed breaks or bits of metal left inside the body. By studying the X‑rays, specialists can work out when the injury happened and help the court understand the full story.
Criminal Cases
An X-ray scan can spot bullets, sharp objects, or other items inside the body. Police and doctors use these pictures to see entry and exit points of a shot or stab. This clear view helps prove how a crime happened and supports evidence in court.
Insurance Claims
An X-ray scan shows insurers the true extent of an injury. This proof removes doubt and speeds up claim decisions. Accurate images help ensure fair payouts for medical costs.
Medicolegal X‑rays as Evidence in Court
In injury or negligence cases, experts use X-ray as evidence in court. It takes clear pictures of injuries and saves them as records. This makes x-ray scans strong proof to support legal claims. They:
- Show injury type and location.
- Date the injury by healing stages.
- Prove or disprove claims of harm.
Impact on Judgments
X‑ray in court can help a judge or jury by showing injuries in clear detail. In 2024, the NHS paid private firms a record £216 million to report X-rays and scans because hospitals faced a 30 percent radiologist shortfall. This gap risks delaying important X-ray reports needed for legal cases. Which can slow evidence gathering and affect court decisions Such delays underscore just how vital timely X-ray evidence is for achieving fair and accurate legal outcome.
Expert Testimony and Reports
Radiologists don’t just supply scan images. They write detailed reports that tie findings to medical standards. In court, they explain how an injury occurred and its severity in simple words. Their testimony adds weight and guides judges.
Digital Preservation and Access
Unlike memories, digital X‑rays stay unchanged in (PACS) picture archiving communication systems. These systems keep a clear chain of custody. This permanence makes X-ray in court evidence hard to dispute. Images and reports stay intact through appeals and reviews. Easy access means evidence can be shown even years later.
Key Benefits of X‑Ray Imaging in Legal Proceedings
By far, it is clear that X-rays have a vital role in legal proceedings. Below are the key benefits of X-ray scans and reports, when presented in courts:
Speedy Evidence Gathering
An X-ray scan delivers clear images in minutes, so legal teams receive evidence quickly. Quick scans help set a clear timeline and guide court actions.
Visual Documentation of Injuries
An X-ray scan highlights bones and soft tissue in high contrast. In injury claims or accident cases, these images show breaks or hidden damage without guesswork. Judges and juries use this proof to determine liability and award fair compensation.
Patient Comfort and Compliance
An X-ray scan is painless and needs no cuts or needles. You stay still for only a few seconds while the scan is being conducted. This ease helps clients, witnesses, or claimants finish the test, even after trauma, ensuring reliable evidence.

Easy Access and Record Keeping
Most clinics and hospitals offer an X-ray scan, so there’s little wait for both NHS and private care. The images feed directly into medical records, ready to attach to legal files as court exhibits.
Want to know which scan is better?
Limitations of X-Ray Evidence
Interpretation Issues
X-ray images can sometimes be hard to read if the scan is blurry or the body parts overlap. Different experts might give different opinions on the same image. This can lead to confusion in court about what the scan really shows.
Potential for Misuse or Misinterpretation
An X-ray scan can be taken out of context or shown without the full medical story. Lawyers or witnesses might overstate what the image proves. This risks leading judges or juries to the wrong conclusion.
Legal Standards and Admissibility
Courts only accept an X-ray scan if it follows clear rules. These include proof that the machine was checked and the scan kept safe from tampering. Lawyers also must show that the person reading the scan is a certified expert with the right training.
Safety and Hazards
Below is an overview of the main risks and safety measures for X-ray use:

X‑Ray Hazards
X‑rays use ionising radiation that can harm cells and DNA over time. Technicians follow ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) rules to keep doses low. Shields and limits protect patients and staff.
Why Are X‑Rays Harmful
High dose X-rays or repeat scans may raise cancer risk, especially in kids. Pregnant women must avoid scans unless essential. Modern digital systems cut doses by up to 60 percent compared to old machines.
Reducing Radiation Risk
To avoid risk wear lead aprons and thyroid collars. Use collimators to narrow the beam. Strict scheduling avoids repeat scans. Regular maintenance and dose checks ensure safe use.
Cost and Accessibility in the UK
Here’s a quick look at X-ray prices and how to access scans in the UK:
Private X‑Ray Services
A private X‑ray often has shorter wait times and flexible hours. Clinics offer digital or portable scans, even on weekends. Fast service helps legal teams meet deadlines and supports urgent care.
Cost of X‑Ray UK
The cost of X-ray in the UK varies by provider. NHS scans are free with referral. Private scans range from £50 to £200 per view. Always check your insurer’s cover to avoid surprise bills.
The Critical Role of X‑Ray Scans in Legal and Medical Contexts
The X-ray scans remain essential to health care and justice. These images provide clear, objective evidence for both clinical diagnoses and courtroom proceedings. These scans give clear proof of any injury or a disease. Knowing why X-rays are harmful, the advantages of an X-ray, and the cost of X-ray in the UK helps you choose wisely. Whether via the NHS or private X‑ray, safe, reliable imaging supports both treatment and justice.
Schedule your next X-ray scan with Concise Medico for fast, expert imaging and medico‑legal support.
Contact us for expert consultation services and detailed medico‑legal X‑ray reports.




