TABLE OF CONTENT
Did you know that over one million people report to UK hospital emergency departments each year for different injuries? In the UK, trauma surgery is usually carried out in major trauma centres when a serious injury needs urgent surgical care. That’s where trauma surgery comes in.
Trauma surgery is a specialised medical procedure dealing with the treatment of traumatic injuries through surgery. Not every trauma needs surgery. However, deep cuts, injuries to internal organs and bone damage can require surgery. Waiting in such cases can be fatal.
This blog explains all about trauma and surgery. Their relation and effects.
Key Takeaways
- Trauma surgery is done to treat injuries.
- It is used to treat severe bleeding and internal organ damage mainly.
- Early surgery increases survival chance.
- Surgery is not required for all injuries.
- Modern surgery trauma care saves thousands of lives each year.
What Is Trauma Surgery?
Trauma surgery is the emergency surgery performed after serious physical injury. Such injuries can happen due to a number of causes, such as:
- Car crashes.
- Accidents.
- Falls from height.
- Violence.
- Serious sports injuries.
- Workplace accidents.
- Fires and explosions.
Such injuries cause damage to multiple organs at the same time. That is why special care and big decisions are needed during surgery.
Trauma surgeons are trained to work fast and stay calm. They can treat multiple organs at the same time.
When Is Trauma Surgery Needed?
Surgery is done when the patient is at risk of losing their life due to injuries. The goal is always to save life, stop damage, and prevent death.
Given below are some of the main reasons surgery becomes necessary.
1. Uncontrolled or Internal Bleeding
Heavy bleeding is one of the most common results of severe trauma. It can be fatal if left unchecked. That is why heavy bleeding often requires surgery. These can include:
- Bleeding that cannot be stopped with pressure.
- Internal bleeding that is not visible.
- Blood loss that causes shock.
Doctors look for signs such as:
- Low blood pressure.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Pale or cold skin.
- Unconsciousness.
Surgery is needed to:
- Locate the source of bleeding.
- Repair damaged blood vessels.
- Remove severely damaged tissue.
If early surgery is not performed, the patient may lose their life.
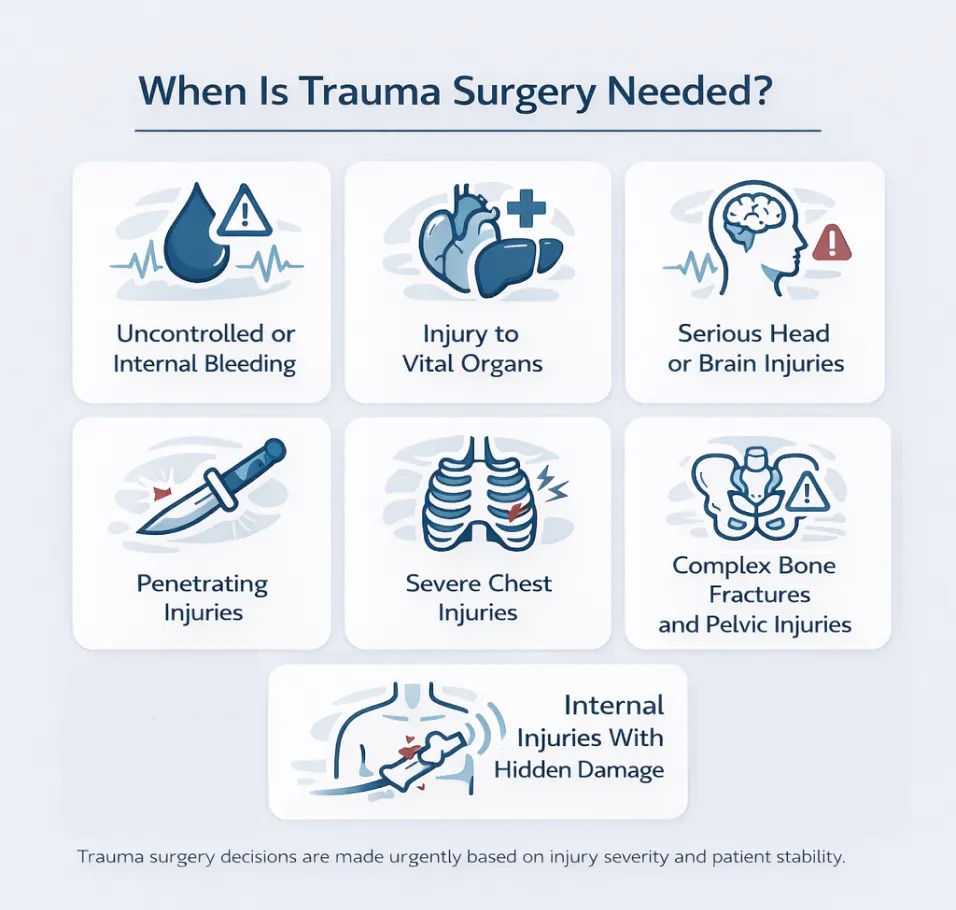
2. Injury to Vital Organs
Vital organs are important, protected structures within the body. Traumatic damage can cause serious damage to vital organs. Vital organs are:
- Lungs.
- Liver.
- Spleen.
- Heart.
- Kidneys.
- Brain.
Any damage to these organs requires quick surgery. If not done in time, it can result in death.
Some examples of internal organ injury are:
- A collapsed lung that stops breathing.
- A torn liver causing massive internal bleeding.
- A ruptured spleen bleeding internally.
With such severe damage, surgery becomes a necessity.
3. Serious Head or Brain Injuries
Head injuries are very common. Around 200,000 people every year are admitted to hospitals for head injuries in the UK. Head injuries can result in serious complications that can go undetected in initial examination. CT scans and MRI are the techniques used to detect issues within brain.
Doctors may choose surgery if there is:
- Bleeding inside the skull.
- Swelling of the brain.
- Fractured skull pressing on brain tissue.
Possible surgical actions include:
- Removing blood clots.
- Reducing pressure inside the skull.
- Fixing fractures.
Surgery and trauma care play an important role in treating brain injury.
4. Penetrating Injuries
When an external object enters and causes trauma, it’s called a penetrating injury. Such injuries are mostly a result of violence such as:
- Knife wounds.
- Gunshot wounds.
- Glass or metal penetration.
Even small entry wounds can hide severe internal damage.
Surgery is required to:
- Remove foreign objects.
- Repair damaged organs.
- Stop internal bleeding.
- Treat infection.
Even a small wound can penetrate deep into the body. The internal damage can be very dangerous. It must be treated by surgery.
5. Chest Injuries
Chest trauma affects breathing and blood circulation. Blunt force trauma, accidents and falls can all cause serious damage to the chest. Examples are:
- Broken ribs puncturing the lungs.
- Bleeding around the heart.
- Major damage to the chest wall.
Doctors may need trauma surgery to:
- Restore proper breathing.
- Control bleeding.
- Prevent heart and lung failure.
Blood circulation and breathing is absolute necessity for life. Any injury that hampers these activities must be dealt with quickly.
6. Complex Bone Fractures and Pelvic Injuries
A bone fracture is common enough. Some fractures require surgery, such as:
- Open fractures.
- Pelvic fractures.
- Fractures damaging nerves or blood vessels.
- Multiple fractures caused by high-impact accidents.
Fractures occur frequently in high-speed accidents and falls. Pelvic injuries specifically require surgery. They can be very dangerous.
7. Internal Injuries With Hidden Damage
Many internal injuries are very hard to detect. Trauma, such as abdominal injuries, can have hidden symptoms. Some examples are:
- Internal bleeding.
- Organ tears.
- Hidden fractures.
To detect such injuries, doctors rely on:
- CT scans.
- Ultrasound.
- MRI.
- Blood Tests.
Even for mild symptoms, the images shown by such techniques can show damage to organs such as the liver, bowel, or spleen. Such damage requires immediate surgery.
How Do Doctors Decide on Performing Trauma Surgery?
In emergencies, doctors follow a system called ABCDE:
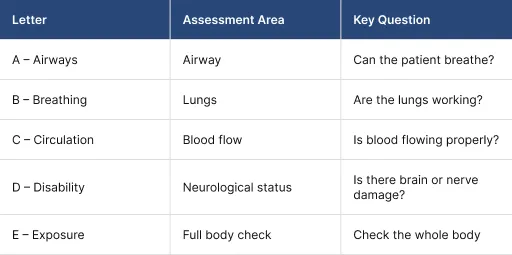
If any part of ABCDE shows a serious problem, doctors act quickly. Based on that, they may decide whether surgery is needed.
What Is Damage Control Trauma Surgery?
Sometimes patients are too unstable for long operations. In these cases, doctors use damage control trauma surgery.
The main aims are:
- Stop bleeding.
- Limit contamination.
- Stabilise the patient.
Once stable, further surgery can be done later. This approach is a cornerstone of modern surgery and trauma care.
Case Study: High-Speed Motorcycle Collision
The following case study will show the importance of surgery in saving the life of a trauma victim.
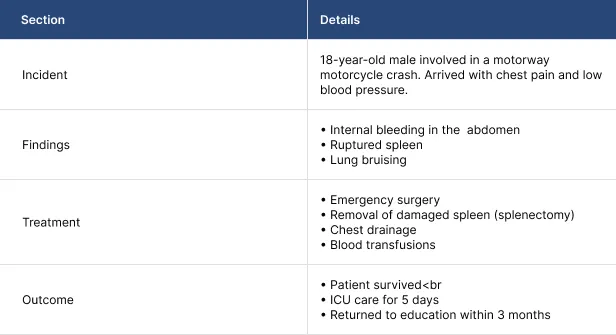
This is how fast surgical decisions can be life-saving.
Importance of Time
“Trauma care is a race against time, where every minute can decide a life.”
- Professor Karim Brohi, UK trauma surgeon.
When you suffer physical trauma, the body starts to fade quickly. An immediate response is needed to bring the body back to normal. Doctors often say: ‘Time lost is life lost’.
Delays can result in:
- Severe blood loss.
- Organ failure.
- Brain damage.
- Shock.
- Death.
Time is of the essence in trauma response. The first 60 minutes after a serious injury are called the ‘Golden Hour’.
During this time:
- Bleeding can still be controlled.
- Organs may still be saved.
- Brain damage may be prevented.
Chances of survival go up if surgery is done withing golden hour.
Recovery After Surgery
Recovery time depends on the nature of trauma.
Common recovery steps include:
- Intensive care monitoring.
- Pain management.
- Physiotherapy.
- Mental health help.
While effects may persist, most patients recover quickly.
Risks and Complications
Surgery is not a risk-free procedure. It comes with its own hazards.
These include:
- Infection.
- Blood clots.
- Organ dysfunction.
- Scarring or chronic pain.
Doctors carefully weigh their options before surgery. With necessary precautions these risks can be reduced.
Why Trauma Surgery Matters
Trauma surgery is not just about operating. It is about:
- Rapid assessment.
- Skilled teamwork.
- Evidence-based decisions.
- Coordinated emergency care.
Together, these elements define effective surgery and trauma systems.
A study by Cureus shows that early surgery prevents complications and improves recovery. This means that surgery does help victims after trauma.
Conclusions
No one plans to need trauma surgery. However, it can happen to anyone. Physical trauma used to be one of the most dangerous things that could happen to someone. Not anymore, thanks to modern medicine, skilled surgeons, and advanced hospitals, survival rates are higher than ever.
At Concise Medico, we understand the importance of surgery in healing trauma. We know when and why it is needed, helping families appreciate the complexity of medical care. Contact us now to get the best in the world of trauma and surgery today.
FAQs
Did you know that over one million people report to UK hospital emergency departments each year for different injuries? In the UK, trauma surgery is usually carried out in major trauma centres when a serious injury needs urgent surgical care. That’s where trauma surgery comes in.
Trauma surgery is a specialised medical procedure dealing with the treatment of traumatic injuries through surgery. Not every trauma needs surgery. However, deep cuts, injuries to internal organs and bone damage can require surgery. Waiting in such cases can be fatal.
This blog explains all about trauma and surgery. Their relation and effects.
Key Takeaways
- Trauma surgery is done to treat injuries.
- It is used to treat severe bleeding and internal organ damage mainly.
- Early surgery increases survival chance.
- Surgery is not required for all injuries.
- Modern surgery trauma care saves thousands of lives each year.
What Is Trauma Surgery?
Trauma surgery is the emergency surgery performed after serious physical injury. Such injuries can happen due to a number of causes, such as:
- Car crashes.
- Accidents.
- Falls from height.
- Violence.
- Serious sports injuries.
- Workplace accidents.
- Fires and explosions.
Such injuries cause damage to multiple organs at the same time. That is why special care and big decisions are needed during surgery.
Trauma surgeons are trained to work fast and stay calm. They can treat multiple organs at the same time.
When Is Trauma Surgery Needed?
Surgery is done when the patient is at risk of losing their life due to injuries. The goal is always to save life, stop damage, and prevent death.
Given below are some of the main reasons surgery becomes necessary.
1. Uncontrolled or Internal Bleeding
Heavy bleeding is one of the most common results of severe trauma. It can be fatal if left unchecked. That is why heavy bleeding often requires surgery. These can include:
- Bleeding that cannot be stopped with pressure.
- Internal bleeding that is not visible.
- Blood loss that causes shock.
Doctors look for signs such as:
- Low blood pressure.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Pale or cold skin.
- Unconsciousness.
Surgery is needed to:
- Locate the source of bleeding.
- Repair damaged blood vessels.
- Remove severely damaged tissue.
If early surgery is not performed, the patient may lose their life.

2. Injury to Vital Organs
Vital organs are important, protected structures within the body. Traumatic damage can cause serious damage to vital organs. Vital organs are:
- Lungs.
- Liver.
- Spleen.
- Heart.
- Kidneys.
- Brain.
Any damage to these organs requires quick surgery. If not done in time, it can result in death.
Some examples of internal organ injury are:
- A collapsed lung that stops breathing.
- A torn liver causing massive internal bleeding.
- A ruptured spleen bleeding internally.
With such severe damage, surgery becomes a necessity.
3. Serious Head or Brain Injuries
Head injuries are very common. Around 200,000 people every year are admitted to hospitals for head injuries in the UK. Head injuries can result in serious complications that can go undetected in initial examination. CT scans and MRI are the techniques used to detect issues within brain.
Doctors may choose surgery if there is:
- Bleeding inside the skull.
- Swelling of the brain.
- Fractured skull pressing on brain tissue.
Possible surgical actions include:
- Removing blood clots.
- Reducing pressure inside the skull.
- Fixing fractures.
Surgery and trauma care play an important role in treating brain injury.
4. Penetrating Injuries
When an external object enters and causes trauma, it’s called a penetrating injury. Such injuries are mostly a result of violence such as:
- Knife wounds.
- Gunshot wounds.
- Glass or metal penetration.
Even small entry wounds can hide severe internal damage.
Surgery is required to:
- Remove foreign objects.
- Repair damaged organs.
- Stop internal bleeding.
- Treat infection.
Even a small wound can penetrate deep into the body. The internal damage can be very dangerous. It must be treated by surgery.
5. Chest Injuries
Chest trauma affects breathing and blood circulation. Blunt force trauma, accidents and falls can all cause serious damage to the chest. Examples are:
- Broken ribs puncturing the lungs.
- Bleeding around the heart.
- Major damage to the chest wall.
Doctors may need trauma surgery to:
- Restore proper breathing.
- Control bleeding.
- Prevent heart and lung failure.
Blood circulation and breathing is absolute necessity for life. Any injury that hampers these activities must be dealt with quickly.
6. Complex Bone Fractures and Pelvic Injuries
A bone fracture is common enough. Some fractures require surgery, such as:
- Open fractures.
- Pelvic fractures.
- Fractures damaging nerves or blood vessels.
- Multiple fractures caused by high-impact accidents.
Fractures occur frequently in high-speed accidents and falls. Pelvic injuries specifically require surgery. They can be very dangerous.
7. Internal Injuries With Hidden Damage
Many internal injuries are very hard to detect. Trauma, such as abdominal injuries, can have hidden symptoms. Some examples are:
- Internal bleeding.
- Organ tears.
- Hidden fractures.
To detect such injuries, doctors rely on:
- CT scans.
- Ultrasound.
- MRI.
- Blood Tests.
Even for mild symptoms, the images shown by such techniques can show damage to organs such as the liver, bowel, or spleen. Such damage requires immediate surgery.
How Do Doctors Decide on Performing Trauma Surgery?
In emergencies, doctors follow a system called ABCDE:

If any part of ABCDE shows a serious problem, doctors act quickly. Based on that, they may decide whether surgery is needed.
What Is Damage Control Trauma Surgery?
Sometimes patients are too unstable for long operations. In these cases, doctors use damage control trauma surgery.
The main aims are:
- Stop bleeding.
- Limit contamination.
- Stabilise the patient.
Once stable, further surgery can be done later. This approach is a cornerstone of modern surgery and trauma care.
Case Study: High-Speed Motorcycle Collision
The following case study will show the importance of surgery in saving the life of a trauma victim.

This is how fast surgical decisions can be life-saving.
Importance of Time
“Trauma care is a race against time, where every minute can decide a life.”
- Professor Karim Brohi, UK trauma surgeon.
When you suffer physical trauma, the body starts to fade quickly. An immediate response is needed to bring the body back to normal. Doctors often say: ‘Time lost is life lost’.
Delays can result in:
- Severe blood loss.
- Organ failure.
- Brain damage.
- Shock.
- Death.
Time is of the essence in trauma response. The first 60 minutes after a serious injury are called the ‘Golden Hour’.
During this time:
- Bleeding can still be controlled.
- Organs may still be saved.
- Brain damage may be prevented.
Chances of survival go up if surgery is done withing golden hour.
Recovery After Surgery
Recovery time depends on the nature of trauma.
Common recovery steps include:
- Intensive care monitoring.
- Pain management.
- Physiotherapy.
- Mental health help.
While effects may persist, most patients recover quickly.
Risks and Complications
Surgery is not a risk-free procedure. It comes with its own hazards.
These include:
- Infection.
- Blood clots.
- Organ dysfunction.
- Scarring or chronic pain.
Doctors carefully weigh their options before surgery. With necessary precautions these risks can be reduced.
Why Trauma Surgery Matters
Trauma surgery is not just about operating. It is about:
- Rapid assessment.
- Skilled teamwork.
- Evidence-based decisions.
- Coordinated emergency care.
Together, these elements define effective surgery and trauma systems.
A study by Cureus shows that early surgery prevents complications and improves recovery. This means that surgery does help victims after trauma.
Conclusions
No one plans to need trauma surgery. However, it can happen to anyone. Physical trauma used to be one of the most dangerous things that could happen to someone. Not anymore, thanks to modern medicine, skilled surgeons, and advanced hospitals, survival rates are higher than ever.
At Concise Medico, we understand the importance of surgery in healing trauma. We know when and why it is needed, helping families appreciate the complexity of medical care. Contact us now to get the best in the world of trauma and surgery today.